Green Infrastructure 2014 Group M - Case Study 2
---> back to group page working group M
please add your title here
| Name | Green roof | |
| Country | Iran | |
| City | Tehran | |
| Authors | Masoumeh | |

| ||
|
| ||
Rationale: Why is this case interesting?
Please explain in short why this site has green infrastructure potential and what makes it special (150 words approx) Rapid urban expansion over the past two decades in Tehran resulted from a high population growth rate and increased rural, urban migration combined with a strong tradition of centralization in the capital .4000 people die each year in Tehran from diseases caused by air pollution, ISNA news agency reported. Moreover, the pollution created by emissions from power generation increases absorption of radiation in the boundary layer (Oke 1982) and contributes to the creation of inversion layers. Tehran's air pollution is below the world standards and the government of the Islamic Republic of Iran identified the pollution as a high priority environmental and health challenge. It is known that between 65 to 70 percent of total emissions are related to urban transport operations . Therefore, Green roofs could be one of the spatial solutions to solve such a big environmental problem.
Author's perspective
what is your professional/educational background and your relation to the site?
I have been graduated with a BA in Architecture. At the moment, I am a master of landscape architecture student(IMLA). Actually, I am from Qazvin and grew up in Qazvin with a Mountain climate.whenever I traveled to Tehran, I was always thinking about how people can be alive in such a intense air pollution. I know the site well. It contain of plenty of different problems because of less of greenery and urban expansion.
Landscape and/or urban context of your case
- Biogeography, cultural features, overall character, history and dynamics
- Illustrations: maps; sketches; short descriptive analyses
- Illustrations
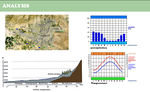
The overall structure of Tehran region, 'is three geographical factors which have an important role in climate. These factors include the Alborz mountain range in the north, west wind flows and Desert in Southern of Province. Height factor plays an important role in the Tehran climate. Minimum precipitation in the northern mountain is more than 500mm but the southern part decreasing and in the margins of Qom Salt Lake reaches 100 mm. October to March is the rainy season in the region. Peak rainfall in January but early spring is low. Usually does not rain in July and August. The hottest months are June, July, August and the coldest are December, January and February. Tehran prevailing wind (270 °) and an average speed of 5.5 m/s. A Tehran cold season usually starts in December and the highest temperature of the year is in midsummer (July).
ANALYZE AND PREDICT THE EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE IN THE GREEN AREA OF TEHRAN
Increased air temperature is a cause of increased respiration and transpiration of plants, Thus, increase usage of more water for irrigation and finally to maintain an optimal state of vegetation. Different plants need different amount of water, it depends on plant species, age and growth. Development of exciting green spaces in Tehran in order to achieve international standards of urban green space will enhance the existing vegetation, which means increased need for water resources. With regard to the semi-arid climate of Tehran and restrictions on water supply, it is necessary that urban green space management strategies to compatible with the changes that have occurred and the future trend will be intensified. Accordingly, vegetation management, platform development and its benefits should be reconsidered.
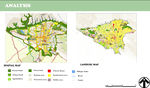
URBAN CONTEXT
IMPORTANT EFFECTIVE ELEMENTS IN TRANSFORMATION Nowadays, Land area can be divided into three distinct sections. First, organized structure such as Towns, Residential fabric and urban users. Second, Network communication and third, agricultural fields, green area and barren area. Rapid population growth, have crowded out vegetation and trees in Tehran. Agricultural field, open land and vegetation replaced with high buildings, roads, highways and other infrastructure. As a result of this change is obvious in the materials, Water bodies and urban green surfaces replaced with densely built-up areas. Surfaces that were once dewy and permeable generally become dry and water-repellent. Lack of porosity materials on urban surfaces and natural vegetation in Tehran has created an evaporation deficit in the city.
Analytical drawings
- Please use analytical drawing for visualising the conflicts/potentials of your site
- Analytical Drawings
Green Infrastructure benefits for this site
Look again at the multiple benefits of green infrastructure - what could be achieved in your site and which are most relevant? GREEN ROOFS
can benefit the urban climate, the microclimate as well as the indoor climate of buildings beneath them. Both intensive and extensive rooftop gardens can play a positive role in these areas. Implementing of the two types is not the same due to the differences in their constitutions. Up to 30oC reduction of roof surface temperature can be achieved. Green roof can also reduce ambient air temperature although the effect is fairly localized according to the studies. Significant differences of around 2oC can be observed although extremes of up to 4 to 5oC could be observed underneath the plants. Denser plants can offer a better evaporative cooling impact to the surrounding while a thick growing medium works like extra insulation to building roofs.
Table1.The impact of green roofs on temperature
Temperature reduction(Degree C)
Surface temperature 10-30
Ambient air temperature 2
Indoor air temperature 2-5.1
The most common type of green roof used in Iran is extensive. They are implemented for different reasons, including storm water management, reducing the urban heat island (UHI) effect, the opportunity to add biodiversity value to the city and beautification of urban roof top landscapes. In order to get higher benefits, the plants of green roofs have to remain alive.as illustrated in figure 30, the implemented extensive green roof detail in Tehran, IrYou can see the picture of Green roof detail which is implemented in Tehran
POSITIVE IMPACT OF GREEN ROOF
• Improved favorable space for residents and aesthetic value • Is possible to plant different kind of flowers, vegetation and fruits • Mitigate urban heat island • Purify the weather and reduce CO • Reduce flood • Absorption of rainwater, Plants that cover the roof can absorb up to 75% of rainwater. • Enhanced storm water management and water quality.
Potential for multifunctionality
Green infrastructure has typically multiple functions. What could be achieved for your site in this respect?
Multifunctionality is one of the key attractions of Green Infrastructure.
its ability to perform several functions on the same spatial area.
• create healthier urban environments but also to manage water • Protecting ecosystems functioning and biodiversity • promoting ecosystem services • Supporting the development of a green economy and sustainable land
Projective drawings
- How would you like this case to change in the near future? (in 1-2 years)
- you may add a short explanation here
Tehran’s climate will become warmer during this period. Annual mean temperature in Tehran and Tehran's night temperature will increase. On the one hand people have high eager to add some greenery on their own building, on the other hand, the price of property is increasing intensely.
- And how could it look like in 10-15 years?
- you may add a short explanation here
- Projective Drawings
- Yourdrawing.jpg
projective drawing
- Yourdrawing.jpg
projective drawing
- Yourdrawing.jpg
projective drawing
.
Summary and conclusion
In recent 20 years, a large number of green lands were converted into lands for Construction Finally, what appears true is that the providing different kind of greenery is an effective solution to reduce the air pollution and temperature. Green roof contributed to mitigate the indoor temperature more. Green roof offer ecological, aesthetic and economic advantages.(green roof system).
Image Gallery
Please add further images/photos here
- Image Gallery
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
References
- please add your references here
1.Lee, D.O., (1984), “Urban Climates”. Progress in Physical Geography, 8(4), pp.1-31
2.Gehl ,Jan , (1987),life between building, using public space,Nem w York,Van Nostrnd Reinhold
3.John Marzluff, Eric Shulenberger, Wilfried Endlicher, marina Alberti, Gordon Bradley, Clare Ryan, Craig ZumBrunnen, Ute Simon(.ed), Urban Ecology: An International Perspective on the Interaction Between ,2008,Springer Science+Business.LLC,p250
4.Gartland, Lisa,(2011),Heat Islands: understanding and mitigating heat in urban areas,UK and USA,Earthscan,2088
5.Arnfield, 2003; Oke, 2006;Souch & Grimmond, 2006 6. Shamsipur Aliakbar ,Tehran Unversity, Geography faculty,
7.http://www.greenroofstoday.co.uk/environmental-benefits-of-green-roof-systems.html
8.http://coolroofs.org/resources/home-building-owners
10.google.de (for photoes)
About categories: You can add more categories with this tag: "", add your categories