Group H - Collaborative Climate Adaption Project
| Place | Amsterdam | |
| Country | Netherlands | |
| Topic | Effects of climate change and adaptation possibilities - case study from Amsterdam, Netherlands | |
| Author(s) | Sonja Jankovic, Zhang Yanjing, Martin Antonov | |

| ||
|
| ||
Rationale: Why have you selected this case study area?
One of the biggest problems caused by climate changes is raising sea levels. For the coastal countries, like Netherlands, this problem could be devastating. Damages will affect residential areas, industrial areas and not at least the environment.
The province North Holland in which Amsterdam is located could face severe floods caused and effected by the future raising sea levels. This is mainly because the whole province is below sea level. In response the Dutch lounged the Delta project. The plan was to construct a large series of outer sea-dikes, inner canal and river dikes to protect this fragile land from disastrous flooding brought by the constant pressures that the North Sea applied. All would be supported by gigantic pumping stations designed to control and protect ground water levels.
We selected this case study area because:
- To rethink the solutions which are applied on to this moment
- To monitor concepts taking place now, and share opinion
- To develop own vision on this what adaptation and mitigatory methods should be applied
- To focus on another problems driven by climate change
Authors' perspectives
Landscape architecture is closely linked with the nature, and so with the climate. It is crucial mentioning, esspecially nowadays, when the climate is changing dramatically. As a landscape architects, we have unique skills which are mixture of landscape planning, landscape design and ecollogy. All these skills we will apply on this case study area, in order to find a solution for global climate change and all the consequences that it brings. We will focus on the preservation of historical and cultural heritage of Amsterdam, by using natural materials and elements that will be effective in reducing the negative consequences of climate change, and also will not endanger the image of the landscape.
Landscape and/or urban context
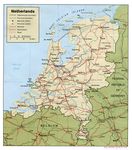
Amsterdam is the the capital of the Netherlands and largest city with a population of more than 750,000. It is located in the province of North Holland in the west of the country. At first, Amsterdam was a small fishing village, founded around the 13th century, when fisherman living along the banks of the River Amstel built a bridge across the waterway. Wooden doors on the bridge served as a dam, so the Amsterdam's name is derived from Amstelredamme, indicative of the city's origin: a dam in the river Amstel. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amsterdam#Cityscape_and_architecture). During the 17th century (also known as Dutch Golden Age), Amsterdam became one of the most important ports in the world and centre of world economy. In the same century Amsterdam got most of the current canals, by which it is known today (as "Venice of the North"). At that time canals were built in a form of three concentric semi-circular canals around the old city center. Developing of the city brought the formation of many streets and smaller canals which intersected the three main canals. That created 90 islands and 1.280 bridges. (http://www.aviewoncities.com/amsterdam/canals.htm). The oldest bridge is Torensluis which was completed in 1648 and is still in its original state. In 2010, the canal district was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List. Part of what makes this district so unique is the canal houses, mostly built in 17th century, as well as the canals. These town houses served as homes as well as workplaces. Except the canals, Amsterdam have two major rivers – Amstel and IJ (which was once a major shipping harbour). Population The Netherlands is the most populated country in the world with 477 people per square kilometer of the land. Amsterdam has a population of 800,000 inhabitants, of which 49.5% Dutch and 50.5% foreigners (which tells us that Amsterdam is open and tolerant society). Transport The Netherlands has an excellent infrastructure of ports, airports, and roadways. In the city of Amsterdam, especially in its center, driving a car is discouraged, mostly by expensive parking fees and many streets are closed to cars or are one-way. There are sixteen tram lines, and four metro lines. Also, three free ferries carry pedestrians and cyclists across the IJ to the North of Amsterdam. Amsterdam has ten railway stations. Cycling is the most popular mode of transportation in the city. Flat land surface allows movement without barriers. Amsterdam is known as bicycle-friendly city with strong bicycling culture, and all the necessary infrastructure to support it (such as bike racks and bike paths – around 400km of bike paths). Bicycles are used by all socio-economic groups. (http://amsterdam.wiki.cliffordtatum.com/wiki/Bicycling_Infrastructure).
Cultural/social/political context
- Brief explanation of culture, political economy, legal framework
Illustration: Bullet points, image, background notes
Local Climate
- What are the climatic conditions at present? Have there been extreme weather events in the near past?
Amsterdam is the largest city and the capital of the Netherlands. The city is located in the province of North Holland in the west of the country.
- Which changes are expected? Is there any evidence?
Since the city is in canals, We will focus on flood-as one of the main problems that Amsterdam has today, which will in the future be even more pronounced due to climate changes that are expected, as our core issue. Illustration: Table or time line
Analysis of vulnerability
- If you consider these potential changes - which aspects/functions of your case study would be affected?
Illustration: Map/diagram/sketches/photos/background notes
Proposals for Climate Change Adaption
- How could your case study area become more resilient to climate change?
- Which measures would need to be taken to adapt to the new situation?
- How could you assure sustainability of these measures?
- Please describe 2-3 measures
Proposals for Climate Change Mitigation
- Which measures would need to be taken to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and other drivers of climate change within your case study area?
- How could you assure sustainability of these measures?
- Please describe 2-3 measures
Your scenario
- How will this area look like in 2060?
- Please forecast one potential future development taking climate change into account
Illustration: Map/diagram/sketches photos and background notes
What can be generalized from this case study?
- Are there any important theoretical insights?
- Which research questions does it generate?
- Short statement plus background notes
Image Gallery
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
References
Source of image /http://bs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amsterdam /http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/46/EU_location_NED.png /http://www.vidiani.com/maps/maps_of_europe/maps_of_netherlands/road_map_of_netherlands.jpg /http://www.planetware.com/map/netherlands-kingdom-of-the-netherlands-map-nl-nlreg.htm /http://maps.nationmaster.com/country/nl/1 /http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/europe/lgcolor/nlcolorlf.htm
About categories: You can add more categories with this tag: "", add your categories