Group U - Collaborative Climate Adaption Project: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Evelinakny (talk | contribs) |
Evelinakny (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 140: | Line 140: | ||
=== Analysis of vulnerability === | === Analysis of vulnerability === | ||
* '''Floods''' are common occurrences in Buenos Aires. With its close proximity to the Rio de la Plata, it is '''highly vulnerable area to sea-level rise''', storm surges and intense rainfall, because of the inadequacies in provision for storm and surface drainage. | |||
* '''Most at risk''' areas are the coastal zone, low-lying lands and areas less than five meters above sea level. | |||
* An ambitious plan '''to address flooding''' in Buenos Aires is underway, with support from the World Bank. However, this has not taken into account climate change variables, as it is claims that there is not enough information to allow this. | |||
* One '''long-term worry''' is the threat to the '''Parana Delta''', which is an important part of Buenos Aires’s economy and also important as a natural flood-control mechanism, the growth of the delta has slowed, and erosion and floods may destroy it. | |||
* '''Indicators values for vulnerability components:''' | |||
* '''Sea-level rise in a year''' - 2,1 mm/year | |||
* '''Storm surge''' – the rapid rise in the water level surface produced by inshore falling barometric pressure – 4,5m | |||
* Number of '''cyclones''' in the last 10 years: 2 | |||
* '''Maximum river discharge''' in the last 10 years – 80 000 m2/s | |||
* '''Average foreshore slope''' – 0,08% | |||
* '''Soil subsidence''' – 8 mm/year | |||
* '''Coastal line along the city''' – 46 km | |||
* '''Number of cultural objects in danger when coastal flood occurs''' – 1300 | |||
* '''Population close to coastal line''' – 900 000 | |||
* '''Growing coastal population in the last 10 years''' – 1.2% | |||
* '''Number of shelters''' per km2 – 0.7 | |||
* '''Population with any kind of disabilities''' – 0.36% | |||
* '''People awareness of floods and preparedness''' – 5 (from 10 points) | |||
* '''Recovery time after coastal floods events''' – 50 days | |||
* '''Km of drainage''' – 80 km | |||
* '''Flood hazard mapping and planning in flood-prone areas''' – 4.5 (from 10 points) | |||
* '''Institutional organizations involved in the flood management process''' – 7 | |||
* Uncontrolled planning zone – 0.3% | |||
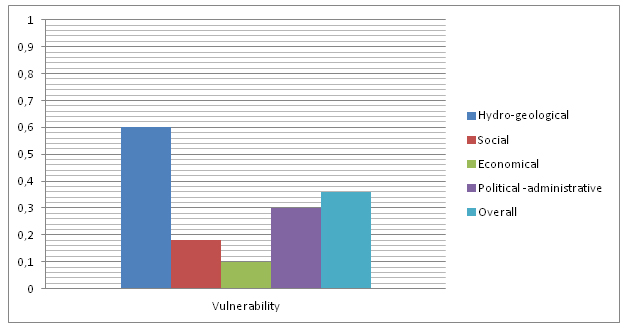
* '''Overall vulnerability index:''' | |||
*The graphic describes the vulnerability of different ranges, evaluated by the indexes from 0 to 1. | |||
[[File:Buen9.jpg]] | |||
=== Proposals for Climate Change Adaption === | === Proposals for Climate Change Adaption === | ||
Revision as of 18:46, 7 January 2013
| Area | Basin vega stream | |
| Place | Belgrano (CABA -Buenos Aires City) | |
| Country | Argentina | |
| Topic | Climate adaptation plan to the city, dealing with the high level of floods | |
| Author(s) | Evelina Knyzelyte, Teodora Morar, Graciela Spelzini | |
|
| ||
Rationale: Why have you selected this case study area?
- Buenos Aires is a vulnerable area that has developed on the basins of streams that has been piped underground. The city grew without an adequate infrastructure and with climate change,it has serious problems to face strong summer rains.
Authors' perspectives
- What theoretical or professional perspective do you bring to the case study?
Landscape and/or urban context
- Biogeography, land use patterns, cultural features, overall character, history and dynamics
- ratio of green/blue and sealed/built-up areas
Illustration: Map; sketches; short descriptive analyses
Cultural/social/political context
Cultural context:
- Buenos Aires from 1880 to 1930 became a multicultural city, ranked with the major European capitals.
- Sometimes the city is called the ‘Paris of South America’, with the highest concentration of theatres, radio, television and cinema.
- The inhabitants of Buenos Aires tend to consider themselves as different from the people of inland Argentina, more European in character rather than Latin American.
- Since the end of the 19th century, Porteños has come to be the name of the people from Buenos Aires. Porteños are generally extroverted, sophisticated, animated, and on the forefront of the latest trends and fashions, yet their attitudes are tinged with pessimism or fatalism about the direction of their country or the latest economic problems. Some Latin Americans have come to view porteñosas slightly arrogant or snobbish.
- Buenos Aires has a long tradition in visual arts, and it hosts many the most important art galleries. It is also very active in the street art and known for ‚The Night of Museums‘.
- The city sometimes is called ‘the city of books‘, as hundreds of bookstores, public libraries and cultural associations are placed here. Every April in the city, the ‚Buenos Aires International Book Fair‘ is celebrated.
- The city has a world-famous zoo and botanical gardens, a large number of landscaped parks and squares, as well as churches and modern architecture buildings.
Social context:
- Population (in 2010): 2 891 082 people.
- Density: 14,000/km2 (37,000/sq mi), in suburbs – 2,400/km2
- Buenos Aires – is the destination for immigrants from Europe, particularly Italy and Spain.
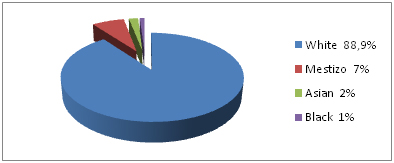
- Racial diversity:
- Mestizos - people of mixed Indian and European ancestry, mainly live in the poorer sections of the city, in the shantytowns, and in the suburbs.
- Belgrano: the 3rd-most populous area in Buenos Aires
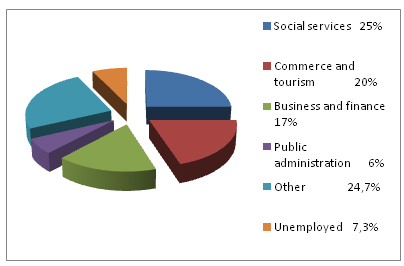
- Employment:
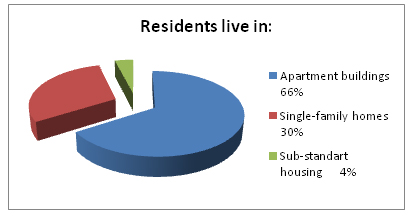
- Accommodation tendencies:
Political context:
- The regional Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of Buenos Aires is US$ 84.7 billion and it comprises about 23% of Argentina’s GDP.
- GDP per capita of 34,200$, when the average of Argentina GDP is about 6.500$.
- Buenos Aires constitutes the 13th largest economy among the world's cities.
- To the west of Buenos Aires is the Pampa Humeda, the most productive agricultural region of Argentina produces wheat, soybeans and corn.
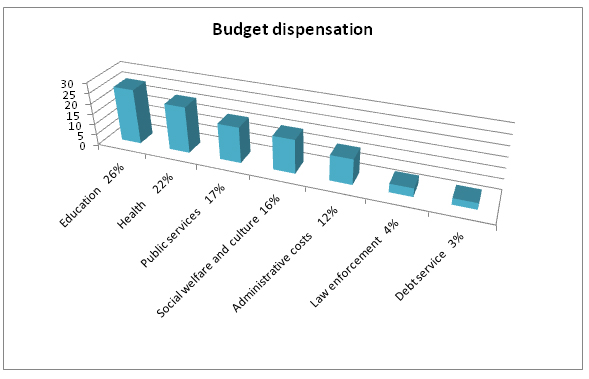
- The city's budget will include US$5.9 billion in revenues and US$6.3 billion in expenditures.
- The city’s budget:
- The Executive is held by the Chief of Government with a Deputy Chief of Government, who presides over the 60-members of Buenos Aires City Legislature.
- By law, the president is responsible for governing the municipality of Buenos Aires, and the National Congress is responsible for legislation pertaining to it.
- The city is divided into administrative units, or communes, each governed by a seven-person citizens’ committee.
Local Climate
Present Climate Conditions:
- Buenos Aires has a humid subtropical climate, with humid summers and mild winters.
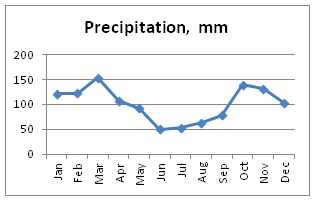
- The city receives 1,242.6 mm of rainfall per year. Rain can be expected at any time of year and hailstorms are not unusual.
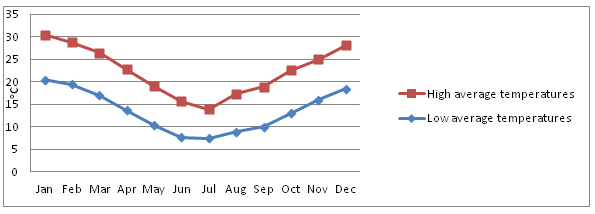
- Annual average temperature - 18 ºC.
- In the summer, the weather is hot and humid. The peaks of temperature could exceed 35ºC. The warmest month is January, with a daily average of 25.1 °C. Humidity is 64–70%.
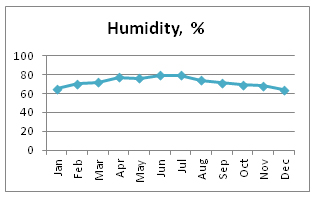
- Autumn and spring are rainy seasons with frequent thunderstorms (from March to June and September to December). Humidity averages is higher than 70%, which brings heavy fogs.
- The coldest month is July. The winter average temperature is 11 ºC, it rarely goes below 0ºC. Cold comes from Antarctica, combined with the high wintertime humidity. Winds influence temperature differences from 10 ºC to 20 ºC.
- Two types of regional winds: the ‘Pampero’ and the Southeast. The Southeast mainly occurs in the autumn and spring. It consists of a strong Southeasterly wind, cool and very wet, which lasts for several days and is often accompanied by constant, light rain. It is expected after a sweltering heat in day.
- The continuous wind makes the flood of the Rio de la Plata rise, while it blocks the water coming from the river into the ocean.
- Annual temperatures changes
- Humidity
- Precipitation
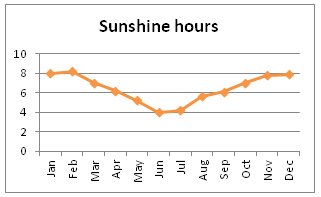
- Sunshine hours
Extreme weather events:
- In 2007 July, Buenos Aires experienced its first major snowfall since 1918 and marked the coldest winter in Argentina in almost thirty years, severe snowfalls and blizzards hit the country.
- In 2010 July, Frigid polar air brought another cold winter with the minimum temperature of -1.5oC. This invasion of cold air covered half of the region with snow, where snow is rare.
- In 2001 August-October Buenos Aires reported almost 250mm of rainfall in October, more than twice the normal amount.
- 2008’s February was the warmest in 50 years. The presence of a dry air mass covering most of central and northern South America inhabited the formation of rain and produced above-normal maximum temperatures.
- Around June 24, in the middle of the winter, the temperatures can reach 24 degrees Celsius. This period is called ‘Veranito de San Juan’.
- ‘Tormenta de Santa Rosa' period on the 30th of August, brings the cycle of rains and thunderstorms that breaks out with the arrival of the spring, at the end of the cold season.
Climate change projections:
- Temperature is intended to increase up to 2.5oC, precipitation 10- 20%
- There has been a general increase in spring and winter temperatures as a result of human influence on climate, making the occurrence of warm seasonal temperatures less frequent.
- In one global-scale study, Argentina was ranked the 5th vulnerable area out of 84 developing countries.
- A sub-national-scale study marked that Buenos Aires could be affected significantly by Sea Level Rise, which will mainly affect areas less than five meters above sea level.
- Climate change will create more flood situations. In 100 years time, the Rio de la Plata is expected to have average water levels that are between 60cm and 1meter higher than today, and stronger winds and storm surges.
- Buenos Aires has also had a significant increase in annual rainfall over recent decades and increasing numbers of intense rainfall events (with over 100mm in 24 hours).
- There is some confidence that there has been a small increase in annual total precipitation between 1960 and 2003 over the central and northern region of the country.
Analysis of vulnerability
- Floods are common occurrences in Buenos Aires. With its close proximity to the Rio de la Plata, it is highly vulnerable area to sea-level rise, storm surges and intense rainfall, because of the inadequacies in provision for storm and surface drainage.
- Most at risk areas are the coastal zone, low-lying lands and areas less than five meters above sea level.
- An ambitious plan to address flooding in Buenos Aires is underway, with support from the World Bank. However, this has not taken into account climate change variables, as it is claims that there is not enough information to allow this.
- One long-term worry is the threat to the Parana Delta, which is an important part of Buenos Aires’s economy and also important as a natural flood-control mechanism, the growth of the delta has slowed, and erosion and floods may destroy it.
- Indicators values for vulnerability components:
- Sea-level rise in a year - 2,1 mm/year
- Storm surge – the rapid rise in the water level surface produced by inshore falling barometric pressure – 4,5m
- Number of cyclones in the last 10 years: 2
- Maximum river discharge in the last 10 years – 80 000 m2/s
- Average foreshore slope – 0,08%
- Soil subsidence – 8 mm/year
- Coastal line along the city – 46 km
- Number of cultural objects in danger when coastal flood occurs – 1300
- Population close to coastal line – 900 000
- Growing coastal population in the last 10 years – 1.2%
- Number of shelters per km2 – 0.7
- Population with any kind of disabilities – 0.36%
- People awareness of floods and preparedness – 5 (from 10 points)
- Recovery time after coastal floods events – 50 days
- Km of drainage – 80 km
- Flood hazard mapping and planning in flood-prone areas – 4.5 (from 10 points)
- Institutional organizations involved in the flood management process – 7
- Uncontrolled planning zone – 0.3%
- Overall vulnerability index:
- The graphic describes the vulnerability of different ranges, evaluated by the indexes from 0 to 1.
Proposals for Climate Change Adaption
- How could your case study area become more resilient to climate change?
- Which measures would need to be taken to adapt to the new situation?
- How could you assure sustainability of these measures?
- Please describe 2-3 measures
Proposals for Climate Change Mitigation
- Which measures would need to be taken to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and other drivers of climate change within your case study area?
- How could you assure sustainability of these measures?
- Please describe 2-3 measures
Your scenario
- How will this area look like in 2060?
- Please forecast one potential future development taking climate change into account
Illustration: Map/diagram/sketches photos and background notes
What can be generalized from this case study?
- Are there any important theoretical insights?
- Which research questions does it generate?
- Short statement plus background notes
Presentation Slides
- Addnewimagename.jpg
Slide One
- Addnewimagename.jpg
Slide Two
- Addnewimagename.jpg
Slide Three
Image Gallery
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
- Yourimage.jpg
your image text
References
Please add literature, documentations and weblinks
About categories: You can add more categories with this tag: "", add your categories