Green Infrastructure 2014 Working Group B - Case Study 1: Difference between revisions
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
<gallery caption= "Localization and structure of Modlin Fortress" widths="150px" heights="150px" perrow="4"> | <gallery caption= "Localization and structure of Modlin Fortress" widths="150px" heights="150px" perrow="4"> | ||
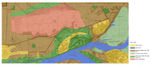
Image:Ma.jpg|Localization of the study case | Image:Ma.jpg|Localization of the study case | ||
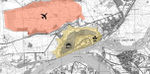
Image:Uol.jpg|proportion between grey and green areas inside the object and location of the airport | |||
Image:Uz1.jpg|proportion between grey and green areas inside the object and location of the airport | Image:Uz1.jpg|proportion between grey and green areas inside the object and location of the airport | ||
Image:Mapatwierdza1.jpg|Explanation of fortress structure | Image:Mapatwierdza1.jpg|Explanation of fortress structure | ||
Revision as of 21:12, 30 November 2014
---> back to group page working group B
Modlin Fortress and its surroundings as a GI potential area
| Name | Modlin Fortress | |
| Country | Poland | |
| City | Modlin (near Warsaw) | |
| Authors | Zuzanna Banaś | |

| ||
|
| ||
Rationale: Why is this case interesting?
Construction of the fortress in Modlin was initiated by Napoleon in 1806. Over the years, complex of buildings of the fortress has been extended and used for many military purposes. Currently The Fortress in Modlin doesn't have any important meaning for the army, most of the buildings are devastated and with every passing year the situation is getting worse. However, the complex has an important cultural aspect because it became a museum itself - there is a possibility of visiting the it with a guide.
Implementation of GI elements to the object can be interesting because of few reasons:
- The area is situated at the confluence of two rivers, it's surrounded by many wetlands and natural areas under Natura 2000 program.
- In 2012 in the direct neighbourhood of the fortress an international airport was opened. Construction and existence of this object and its infrastructure has a huge impact on the ecological situation in the entire area. The construction stage was connected to deforestation and destruction of natural habitats of many species, now in the area exists the probability of disorder of the hydrological situation (such as drying of wetlands), soil and water pollution, the problem of noise and artificial illumination. Minimizing the negative effects of the airport construction can be achieved by proper management and development of adjacent areas.
- In 2013 Modlin Fortress has been bought by a private investor. The plans of renovation and adaptation buildings for new functions are already approved. The complex is supposed to become a "smart city", connecting together social, cultural and educational functions (residential zone, hotel, museum of fortress etc). In this case the huge necessity of including development of recreational and sport areas to these plans exists. What's more, for this moment in the city of Modlin (or even in bigger city located nearby) there is no urban park, providing functions mentioned above and other social and cultural benefits
Author's perspective
I have a bachelor in landscape architecture and I can appreciate the ecological meaning and value of nature, which is amazing in the area of Modlin Fortress and its surroundings. Also, as a person who likes to travel I have already become one of many users of the Modlin Airport, which clearly facilitates the air traffic in the Masovian region by relieving Warsaw Chopin Airport. Because of knowing the importance of both mentioned cases, working on integrating areas and providing cooperation between them is interesting to me, mostly thinking of the perspective of expanding urbanization in region.
Landscape and/or urban context of your case
- Biogeography
The area is situated in Eurosiberian region, in east-central Europe and from geomorphological point of view it's Middle European Plain, Masovian Lowland. It means, that the the relief of the terrain in this place is almost flat, rich in very developed river network. The medium altitude of the area is 127,6 m above the see level. Modlin is a district of Nowy Dwór Mazowiecki, located in east-central Poland, in Masovian Lowland. The climate of Masovian lowland is transitional climate between maritime and continental climate. As a resoult in the region there is pretty high temperature amplitude (in a scale of year), mostly during the winter season (2°C to -2°C). In the summer the average temperature is balanced, around 18 °C - 18,5 °C. The atmospheric precipitation level here is the lowest in the country and usually it's less than 500 mm during the year scale. Although soils here are rather poor- mostly podzols- nearby big rivers (so where Modlin Fortress is located) it's easy to find fertile alluvial soils. Despite the fact, that in most of Masovian Province area woods have been replaced by urban structures or transformed into Pinus monocultures, in the surroundings of Modlin still wilderness and various woods exist.
Flora and fauna existing in the area: according to document done towards the needs of Professional Geodety School, I've collected information about species existing in the sourroundings of the airport. Most common vegetation is trees such as: Acer sp, Betula sp, Corylus sp, Crataegus sp, Picea sp, Pinus sp, Populus sp, Prunus sp, Quercus sp, Sanbucus nigra sp, Tilia sp. With other plants mostly we can find there: Lupinus sp, Silybum marianum, Solidago sp, Tanacetum vulgare, Urtica dioica.
- Urban context: history and dynamics
The location of Modlin at the confluence of Vistula, Narew and Wkra rivers was bringing to the place outstanding defensive qualities. Napoleon Bonaparte, during extending his impact on Eastern Europe, created Duchy of Warsaw and built serie of fortresses in its area. One of them was Modlin Fortress, which was started in 1806. According to his plan, the internal circuit of today's citadel was formed. The stronghold was created from earth and wood, with 5 bastions and the shape of semicircle, opened to the river.
After the Napoleon's period, the fortress has been occupied by Russian army. Russians have extended the area of fortress with an external perimeter, which was based on the shape of "crowns" of the internal bastion and consisted six fronts. In 1864 the complex of barracks was built, the citadel and the external circuit have been surrounded by the wall, called the Carnot. Im 1883 another reconstruction started- the Tsar's Army decided to build the "chain" of forts surrounding the fortress. This 8 forts are made of earth and bricks, and its length is 30 km, they are creating the first ring of forts. Similar modernization has been done in 1914, when the second ring of forts appeared. They created 10 additional forts, using concrete and steal.
87 years later, already after the I World War in December 1918 the Modlin Fortress has been taken by Polish Army.
In the interwar period Corps of Cadets stationed in Modlin. There was also Armored Training Center, with the Cadets School and the School of Officers, and also Sapper Training Centre. During next years the complex has been used for military goals, after the II World War the object still has been used by Polish Army as a training area etc.
Nowadays The Modlin Fortress isn't anymore strategic military point. It became a historical monument, with it's well preserved buildings which are attracting many tourists.
- Overall character and cultural features
Nowadays, during the urban sprawl the space between internal and external perimeter of the fortress is partly occupied by housing estates and urban infrastructures. The significant object is an international airport, located just on the border of Modlin Fortress, which for sure is important social and cultural aspect overall, but obviously has a huge ( not always positive) influence on the ecology of the region and the quality of life of local citizens. The area in general is open, but with the historical buildings the situation is different - only some of them are open to the public and people can visit them with the guide, the rest is getting destroyed with the time and acts of vandalism. The terrain of the fortress is subject of conservation officer's care and in spite of the fact, that last year it was bought by private investor, the conservator needs to agree for all the proposed changes. There is a permission of adapting buildings of the main part (citadel) to new functions such as apartments, office space, but there is also condition: not to change overall exterior appearance of the buildings and to keep educational function by reserving part of the fortress for a museum. However labour on renovation of the object will need many changes in underground infrastructure such as connection to canalization, electricity and so on. Also with another extension of urban zone, there will be a necessity of creation social spots, such as parks, public squares and infrastructure connected to this. Fortunately in the area, inside the buildings of citadel and in the area between two perimeters of the fortress, there is a lot of greenery which can be easly adapted to new functions.
- Localization and structure of Modlin Fortress
Analytical drawings
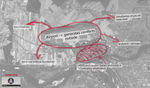
- Please use analytical drawing for visualising the conflicts/potentials of your site
- Analytical Drawings
Green Infrastructure benefits for this site
From the ecological point of view, it's really necessary to keep and provide biodiversity of the region and preserve its habitats, mostly knowing that all around there are areas under protection of different organs (National Parks, Natura 2000 areas, Natural reserves). In this case, ensuring the connectivity and easy access between the areas should be priority. In my site, a big impact on existing ecology have changes, which were introduced to the area 2 years ago (the airport construction), so also the most important relevance are mitigating the effects of changes in the area and the potential of reinforcement of the right direction of its development.
A very important is also social aspect, because of the existence of urban structures and plan of extending it in the study case. Here, the airport is a good factor, contribute to increase of the economic value of the area, which is now very well connected to Warsaw (construction of the airport causes on construction of additional transportation like road infrastructure and railways to provide connectivity between Modlin and the Capital city of Poland). Because of the increasing urbanization of the region, providing green infractructure of the city is inevitable, to improve quality of human life here. Obviously, in case of supplying everything that is necessary to live well in the area we will observe the economical increase there - new jobs opportunities and overall prosperity.
The cultural aspect is also interesting. Taking care about historical values the area represents, it's possible to develop turistic interests of the area. Here I would think about taking into consideration the riverside, where already some restaurants exist. Thinking of the plan of construction of hotel in the area, improving the shore of the river and adapting it to recreational functions seems like a good idea.
Potential for multifunctionality
All the structures planned in the Modlin Fortress have a big potential of multifunctionality. The project of city park or development and well management of river side, beside the fact of being recreational places, can also involve objects with impact of ecological goodness, such like infiltrating vegetation, supporting purifying the rainwater and water of the river, vegetation accumulating pollution and dusts from the air, vegetation representing habitats of many species and increasing biodiversity. Proper use of existing elements of the fortress such like destroyed forts can integrate isolated areas in one big connected area.
Projective drawings
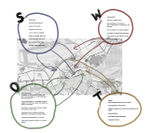
- How would you like this case to change in the near future? (in 1-2 years)
In the near future I hope those existing elements will be rationally used and will develop new functions, which don't require a big changes, f. ex. circuits will become more accessible by creating view points on them and forts, also connectivity will develop by opening the gates and creating new ones. I would like to see already some works which can have impact on increase of biodiversity in the area, replacing lost habitats with new, similar ones, and in general works that should be done in the zone between an airport and fortress area, so zone responsible for minimizing negative airport effects, such as creation of basins with filtrating vegetation (rational rainwater management), noise and illumination barriers made out of trees and dense vegetation, which can also accumulate pollution and so on.
- And how could it look like in 10-15 years?
In 10-15 years I would like to see working "smart city" with everything mentioned above: city park including cultural and educational functions, facilities for citizens, well developed green infrastructure in the area of city park (such as urban agriculture gardens), inclusion and connection of rivers to the complex. All this structures adapted to existing conditions, connected together (providing easy access not only for a society but also without barriers to fauna) by being a continuous strip of habitats and vegetation.
- Projective Drawings
- Yourdrawing.jpg
projective drawing
- Yourdrawing.jpg
projective drawing
- Yourdrawing.jpg
projective drawing
- Yourdrawing.jpg
projective drawing
Summary and conclusion
I' ve chosen the Modlin Fortress because in my opinion it represents objects, where introducing not only one, but many green infrastructure elements is possible and where all those elements are really needed. Considering all the factors mentioned in the study case, green infrastructure can easily affect positively in area and bring here ecological, economical, cultural and social values and thereby cause an increase in the overall value of the site.
Image Gallery
- Image Gallery
References
- please add your references here
http://www.twierdzamodlin.nsk.pl/en/galeria/stare-zdjcia.html?page=1&catpage=1
http://nowy_dwor_mazowiecki.fotopolska.eu/454425,foto.html
http://pl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nizina_Mazowiecka#Klimat
Wincenty Okołowicz: Strefy klimatyczne. W: Atlas geograficzny. [Oprac. red. Henryk Górski, Wanda Jędrzejewska ; red. map: Zofia Cukierska et al]. PPWK Warszawa, Wrocław 1990, Wydanie 23
Janusz Stasiak, Zbigniew Zaniewicz: Geografia. Vademecum maturalne. Wydawnictwo Pedagogiczne „Operon”, Gdynia cop. 2006.
About categories: You can add more categories with this tag: "", add your categories